7 Partnerships

PARTNERSHIPS in Creative Endeavours

In this Chapter:

Introduction: The Power of Partnerships in a Creative World
Imagine walking into a boardroom where everyone thinks just like you. They nod in agreement with your ideas, validate your assumptions, and rarely challenge the status quo. At first, it feels comfortable—maybe even productive. But in reality, it’s a slow march toward stagnation. Without friction, without different viewpoints clashing and combining, there’s no spark. No innovation. No magic.
Now, imagine a different scenario. You’re in a room with a designer from Tokyo, a tech entrepreneur from Berlin, a data analyst from São Paulo, and a logistics expert from Nairobi. Each brings a unique lens to the discussion—one shaped by their cultural background, professional expertise, and lived experience. Suddenly, ideas evolve. Weak concepts are refined. Stronger solutions emerge. That’s the power of diverse partnerships in creative business strategy.
Collaboration isn’t just a feel-good corporate mantra; it’s a necessity in the fast-moving world of entrepreneurship. Successful businesses are built on partnerships—within teams, across industries, and even across borders. From supply chain integrations to global co-branding, from AI-enhanced teamwork to crowdsourced innovation, the best ideas come from the intersection of different minds, skill sets, and perspectives.
The Power of Collaboration in Business Creativity
In today’s hyperconnected world, creativity is no longer a solo act. Businesses that thrive don’t rely solely on internal genius; they pull knowledge, insights, and inspiration from a diverse range of partners. Whether it is brands teaming up with customers to co-create products, companies leveraging AI to enhance ideation, or industries joining forces to solve global challenges or raise the competitive bar, collaboration is the ultimate accelerator of creativity.
Let us consider Lego, the toy bricks (and now various other toys) manufacturing giant. Once on the brink of bankruptcy, the brand turned things around by embracing open-source creativity—engaging customers, licensing partnerships with global franchises (Star Wars, Marvel), and co-creating with external designers through its Lego Ideas platform. This shift from a closed to an open innovation model turned Lego into a creative powerhouse. Today LegoTM is a global entertainment giant with an expanded product portfolio of both product line width (movies, games, toys, and merchandise for movies) and product line depth (various Lego collections such as Friends, Nature, Dimensions).
You can read more here about product lines:
Product Depth and Product Mix: Definition and Examples [2024],
Similarly, Apple’s innovation isn’t just about sleek design—it’s about strategic partnerships up and down the supply chain. Foxconn, TSMC, and dozens of other companies contribute to the iPhone’s creation, while collaborations with software developers drive its App Store ecosystem.
These aren’t just transactions – they are innovation alliances. This type of collaboration has been termed “co-opetition” in business circles. The smartest businesses don’t just compete; they co-create. A notable include is Pfizer and BioNTech. In March 2020 Pfizer and BioNTech jointly developed a COVID-19 vaccine – a prime example of co-opetition. As another example, the Star Alliance of airlines provides a much wider range of options than one airline could. Star Alliance is the first and currently the largest global airline alliance. Its 26 member airlines each have their own culture and service quality, but together they offer a vast network of global travel to 186 countries. Maybe closer to home, your Netflix subscription is hosted on Amazon Web Services.

Overview of the Unified Model of Wisdom and the Role of Partnerships
Great business leaders don’t just rely on intelligence; they rely on wisdom. The Unified Model of Wisdom (which combines insight, sense-making, and creative intelligence) suggests that the best decisions come from multiple perspectives. It’s not about knowing all the answers—it’s about knowing who to ask and how to integrate their expertise into something greater.
In business, this means:
- Listening to customers as co-creators, not just buyers.
- Engaging suppliers as innovation partners, not just vendors.
- Building global alliances that leverage cultural intelligence and market diversity.
- Collaborating with AI as a creative augmentation tool, not a replacement.
Let us consider Unilever, for example. The company’s commitment to cross-border collaboration has allowed it to develop sustainable supply chains, tap into emerging markets, and integrate diverse perspectives into product innovation. By partnering with NGOs, local farmers, and technology providers, Unilever isn’t just selling products; it’s solving global problems through business and helping small business owners to have a steady stream of income, and often access to research and development they would not be able to afford on their own.
The takeaway? Innovation thrives at the crossroads of different perspectives. If you want to build a creative, market-leading business, you need the right partnerships.
The Synergy of Diverse Teams
Embracing Diversity for Enhanced Creativity
Imagine a room filled with individuals from various backgrounds—different cultures, professions, and life experiences. Each person brings a unique perspective, a distinct way of thinking. When these diverse minds collaborate, something magical happens: creativity flourishes. It’s like mixing a palette of vibrant colours to paint a masterpiece that one hue alone could never achieve.
Research supports this notion. A recent study by the Boston Consulting Group found that companies with diverse leadership teams report higher innovation revenue—45% of total revenue versus 26% for those without. The extent to which organizations can thrive in rapidly changing business environments depends largely on the creativity of their workforce. Research increasingly suggests that developing creative solutions to complex organizational problems is rarely the domain of the lone genius but rather requires team creativity. Solving complex problems by generating novel, appropriate and valuable solutions is the terrain of a team of employees and other agents (externals and AI) working together interdependently.
Consider Marriott InternationalTM. The company has long embraced diversity and inclusion, maintaining a strong belief that an array of perspectives within the company drives its innovation and competitiveness. Its inclusive culture contributes to its high performance. The company’s commitment to putting people first and prioritising employee well-being has created a positive and supportive work environment. Another example is Amazon. The company believes that having a diverse workforce gives a better understanding of customers’ needs and is key to unlocking ideas. This diversity helps drive innovation within the company.
Overcoming Challenges in Diverse Collaborations
Of course, bringing together diverse teams isn’t without its challenges. Different perspectives can lead to misunderstandings or conflicts. But these hurdles are surmountable. Encouraging open communication and fostering an inclusive environment where every voice is heard can turn potential friction into fruitful discussions. A study published in the International Journal of Innovation Science (Jones, Chace & Wright, 2020) highlights that while diversity provides a creative advantage for innovation teams, team dynamics play an important role in maximising these advantages.
DIY Activity: Building Your Diverse Dream Team
Now, let’s put this into action. Think about your current team or the team you aspire to build either as a permanent talent cohort or as a matrix of talents from diverse disciplines. Are there diverse perspectives represented (age, education, ethnicity, background in business, exposure to customers)? If not, consider ways to bring in different voices. This could mean employing individuals from various cultural backgrounds, different industries, or hiring experts or part-time team members with unique skill sets (required for a specific project/problem). Create an inclusive environment where everyone feels valued and encouraged to share their ideas. Remember, it’s the blend of these diverse perspectives that will drive your team’s creativity and innovation.
Addressing Communication Barriers and Cultural Differences
Diverse teams may face communication challenges due to language barriers, different communication styles, and cultural misunderstandings. These issues can hinder collaboration and impede the innovation process. In fact, researchers often emphasize that cultural diversity in teams needs careful management due to various inherent problems in diverse teams. Studies emphasize the process losses resulting from reduced perceptions of similarity-attraction among team members; negative biases associated with social categorization processes; feelings of dislike and resentment due to incongruent values; and communication barriers resulting from differences in language and communication styles. The “positive” conclusions include information-processing theory, which holds that diversity may lead to information processing advantages due to team members’ different perspectives, knowledge bases, and decision-making styles, which, if properly harnessed, can enhance creativity and decision-making quality.
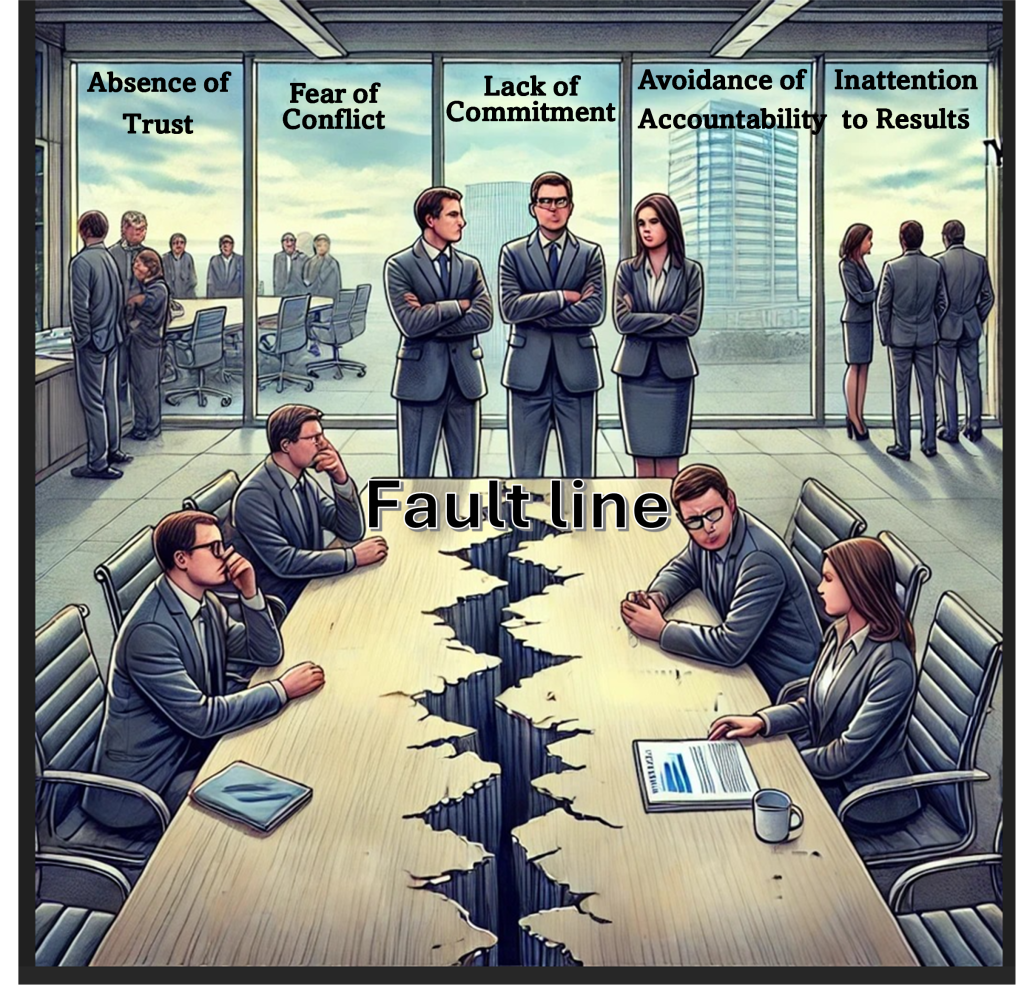

According to creative team research, there are five main reasons why teams encounter problems during operations. They are referred to as five “fault-line” factors: (1) Absence of trust; (2) Fear of conflict; (3) Lack of commitment; (4) Avoidance of accountability; and (5) Inattention to results (Pirola-Merlo, Härtel, Mann, & Hirst, 2002).
To address these challenges, it’s essential to foster an environment where open and respectful communication is encouraged. Providing cultural sensitivity, cultural competency and EQ training can help team members understand and appreciate each other’s backgrounds, reducing misunderstandings and building trust.
Strategies to Foster an Inclusive Team Environment
Creating an inclusive environment where all team members feel valued and heard is crucial for leveraging the benefits of diversity. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Establish Clear Communication Norms: Establish guidelines that promote active listening, respectful dialogue, and equal participation.
- Encourage Collaborative Decision-Making: Involve all team members in the decision-making process to ensure diverse perspectives are considered.
- Provide Diversity and Inclusion Training: Regular training sessions can raise awareness about unconscious biases and promote inclusive behaviors.
- Celebrate Cultural Differences: Recognize and celebrate the diverse backgrounds of team members to foster a sense of belonging. By implementing these strategies, teams can overcome the challenges associated with diversity and harness its full potential to drive innovation. DIY Activity: Building Your Diverse Dream Team
- Create Team-Building Opportunities: Find creative ways to allow team members to get to know each other’s strengths and development areas and allow for social events where they can build trust, loyalty to each other, and a sense of joint purpose and ownership of projects.
Now, let’s put these insights into action. Reflect on your current team composition. Consider the following steps to enhance diversity and foster an inclusive environment:
- Assess Current Diversity: valuate the diversity within your team in terms of cultural backgrounds, professional experiences, and skill sets.
- Identify Gaps: Determine areas where diversity is lacking and consider how these gaps might be limiting innovation.
- Recruit Diverse Talent: When hiring, seek candidates who bring different perspectives and experiences to the team.
- Promote Inclusive Practices: Implement the strategies outlined above to create an environment where all team members feel valued and empowered to contribute.
- Encourage Continuous Learning: Foster a culture of continuous learning where team members are encouraged to share their knowledge and learn from each other. By consciously building and nurturing a diverse team, you can unlock new levels of creativity and drive innovation within your organization.

AI as an Agent in the Creative Co-ignition Chain
To help creators and genii seamlessly integrate AI into their creative processes while maintaining their unique artistic identity, I’ve developed a highly memorable and intuitive model using a mnemonic: C.R.E.A.T.I.V.E.
Each letter represents a key stage in the process of AI-enhanced artistic collaboration. Let’s break it down:
Table 7.1 The C.R.E.A.T.I.V.E. Model for AI collaboration in Artistic Processes
|
Stage |
Description |
|
C – Clarify Your Vision |
Define your objective. What do you want AI to assist with? Is it ideation, composition, enhancement, or something else? Clarity ensures AI serves your artistic intent rather than dictating it. |
|
R – Research & Select AI Tools |
Not all AI tools are the same. Whether it’s DeepDream for surreal visuals, RunwayML, Adobe Firefly, DALL-E2. Pictory.ai, Stable Diffusion, Midjourney for generative art, or Jukedeck or Sora for AI-assisted music, Canva, Filmora.wondershare.net for videos, Stormz for cluster ideas, or Jobalytics, Rezi, or Yoodli for job applications, select the tool that aligns with your vision. |
|
E – Experiment & Generate AI Outputs |
Let AI generate raw material—images, melodies, textures, or concepts. Use multiple iterations and unexpected results as part of the discovery process. AI can surprise and inspire. |
|
A – Augment & Integrate AI Contributions |
AI should be a co-creator, not a replacement. Merge AI-generated content with your work—refine, remix, and personalize outputs to ensure your unique artistic signature remains. |
|
T – Test & Iterate Collaboratively |
AI-generated work should evolve. Seek feedback from peers, mentors, and your audience. Tweak AI contributions to ensure they align with your emotional and artistic intent. |
|
I – Infuse Human Emotion & Storytelling |
The power of human creativity lies in emotion, narrative, and depth. Ensure AI-enhanced pieces resonate with real human experience by adding layers of feeling and meaning. |
|
V – Validate & Finalize Your Creation |
Step back and assess the final piece. Does it reflect your artistic essence and intent? Make necessary adjustments to balance AI precision with human spontaneity. |
|
E – Evolve & Explore Further |
Creativity never stops. Explore new AI tools, experiment with different approaches, and push boundaries. Stay ahead by continuously evolving with AI innovations. |
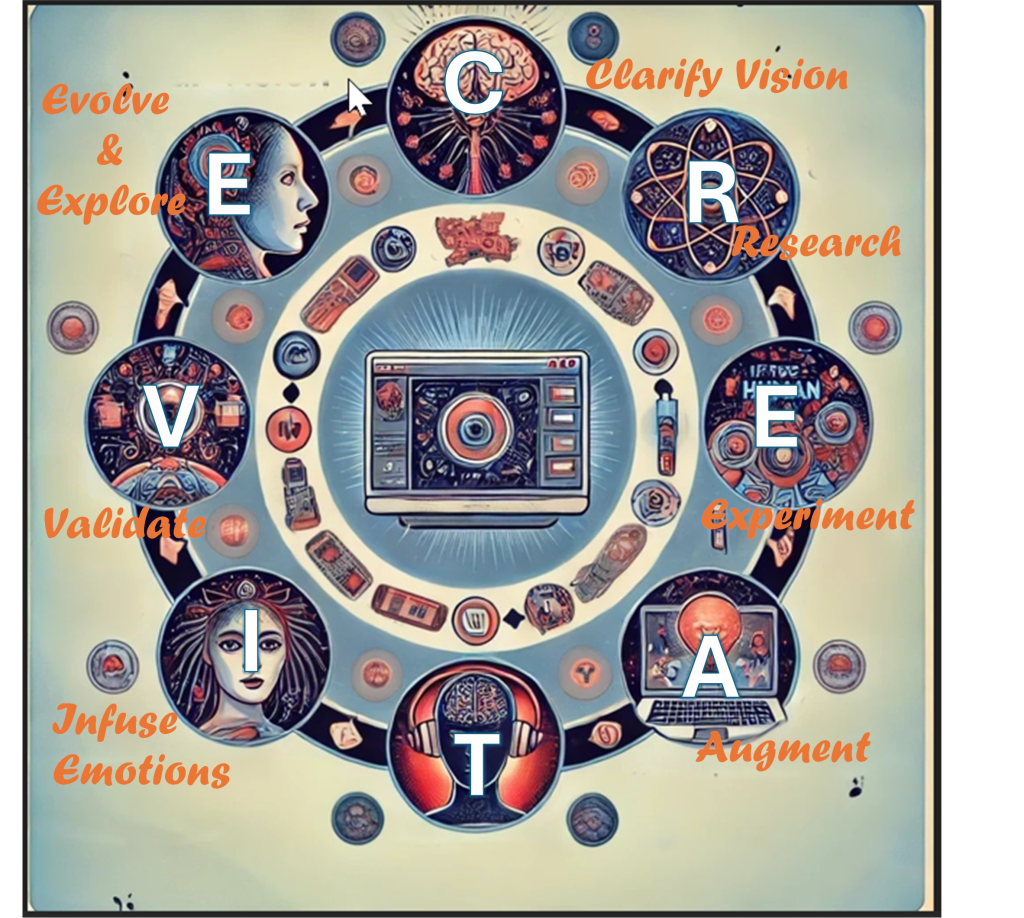
Why use C.R.E.A.T.I.V.E.?
- Easy to remember
- Balances AI capability with human creativity
- Flexible across artistic fields—visual arts, music, writing, design, science, data visualization
- Encourages iteration, refinement, and emotional depth
Case Study: AI in Painting – Refik Anadol’s Data Sculptures
Refik Anadol, a renowned AI artist, follows a C.R.E.A.T.I.V.E. approach:
- Clarifies his vision – using AI to transform massive datasets into immersive visual art.
- Researches and selects tools like machine learning algorithms and GANs.
- Experiments & generates fluid, dreamlike AI outputs.
- Augments & integrates them into physical installations.
- Tests & iterates through real-time audience interaction.
- Infuses emotion, colour, music & narrative to make data feel poetic.
- Validates & finalizes his work before showcasing in galleries worldwide.
- Evolves continuously by incorporating new AI, machine learning models.

The C.R.E.A.T.I.V.E. Model provides a structured, flexible method for working with AI while ensuring the artist’s unique identity remains intact. Rather than seeing AI as a threat, creatives can use it as a sparring partner, idea generator, and co-pilot in artistic exploration.
Integrating AI into the Creative Process
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into the creative process can significantly enhance idea generation and development, offering tools that inspire innovation and streamline workflows. A recent publication and seminar by Matt Kramer, Editor of AllThingsINNOVATION, offers up-to-date insights in the video ‘Reinventing Innovation with Generative AI-Enabled Insights’. As innovation and insights teams ramp up their data-driven strategies, artificial intelligence is emerging as an indispensable ally in product research and development. Tim Joyce, Principal at ZS, and Amanda Beacher, Senior Consumer Insights Manager at The Hershey Company, recently shared their hands-on experiences with leveraging AI tools to drive innovation. You can watch the video of their real-world application here:

Understanding AI’s Role in Idea Generation and Development
AI can augment and enhance humans’ capabilities during every one of the creative stages. In this section we will explore how AI plays a pivotal role in creativity and examine practical applications to enrich your projects.
AI serves as a collaborative partner in the creative process, assisting at various stages:
Inspiration and Brainstorming: AI can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and trends, providing a foundation for new ideas. For instance, AI algorithms can forecast future trends by analyzing historical data, helping businesses proactively generate ideas that align with anticipated market needs.
Content Creation: Generative AI models can produce text, images, music, and more, serving as a springboard for creative projects. Tools like ChatGPT can generate sentences, ideas, or even entire paragraphs that serve as springboards for crafting engaging narratives.
Design and Visualization: AI aids in creating visuals by generating design elements or entire compositions, expediting the design process. For example, AI design tools can assist in graphic design, web development, and video editing by automating repetitive tasks and providing creative suggestions.
Tools/Applications Facilitating AI-Driven Creativity
Several AI-powered tools are available to enhance various aspects of the creative process:
Midjourney: An AI program that generates images from textual descriptions, aiding artists in visualizing concepts.
Artbreeder: A machine learning-based platform that allows users to create and modify images collaboratively, offering a unique approach to visual idea development.
RunwayML: Provides a suite of AI tools for creatives, including real-time video editing and generative design features, streamlining the creative workflow.
ChatGPT: An AI language model that assists in generating text-based content, useful for writers seeking inspiration or assistance in drafting.
Figma: A collaborative design tool for teams. Explore ideas and gather feedback, build realistic prototypes, and streamline product development with design systems
DIY Activity: Embarking on AI-Enhanced Creativity
Objective: Integrate AI tools into your creative workflow to explore new avenues of innovation.
Identify a Creative Challenge: Determine an area in your creative process where you seek enhancement or inspiration.
Select an AI Tool: Choose an AI application relevant to your field (e.g., Midjourney for visual arts, ChatGPT for writing).
Experiment with the Tool: se the AI to generate initial concepts or content. For instance, input a prompt into Midjourney to create a visual representation of your idea.
Refine and Develop: Take the AI-generated output and modify it to align with your vision, adding your personal touch and creativity.
Seek Feedback: Share your work with peers or mentors to gather insights and suggestions for improvement.
Iterate: Use the feedback to make adjustments, possibly using AI tools again for further refinement.
Reflect: Assess how the integration of AI influenced your creative process and the final outcome. By thoughtfully incorporating AI into your creative endeavours, you can unlock new perspectives and efficiencies, enriching your work while maintaining your unique artistic identity.
Navigating Challenges in AI-Augmented Creativity

As young entrepreneurs and genii step into the world of AI-augmented inventions, artistry and creativity, they will be met with opportunities for innovation—and a unique set of challenges. While AI offers transformative tools for creativity, achieving the right balance between human intuition and technological assistance is vital. Let’s explore these challenges and how you can navigate them effectively.
1. Maintaining Artistic Authenticity
When AI-generated content dominates the creative process, it risks overshadowing your unique artistic voice. Your audience connects with the emotional depth and personal touch in your work—something an algorithm can’t replicate. Also, ALWAYS check that the output is on par with your brand, your personal values and your “voice”. Make sure the output reflects the cognitive, emotional and social value you wish to project.
Solution: Use AI as a collaborator, not a replacement. Treat AI outputs as a starting point or raw material that you refine and shape with your personal style. For example, if AI generates a design, modify it to reflect your creative vision. Always check the evidence provided and ALWAYS ask for the sources to be cited so that you, as responsible author/owner/creator can do a background check on the provenance of the art, the authenticity of the sources and the validity of the evidence (credibility of the original source).
2. Avoiding Over-Reliance on AI
AI can streamline your workflow and generate ideas rapidly, but relying too heavily on it might stifle your own creativity. The risk lies in losing the ability to innovate and think critically; skills that remain core to your long-term growth.
Solution: Allocate time for AI-free creative exploration. Develop raw ideas on your own before consulting AI tools, ensuring your originality and instincts stay sharp.
3. Balancing Skill Development
AI tools might tempt you to skip the traditional, hands-on processes of building creative skills. Over time, this can lead to a decline in manual techniques and artistic proficiency, which could limit your versatility and your initiative, and lead to a “mental block” when you have to perform without being able to use AI as copilot or crutch.
Solution: Balance is key. Use AI to complement your traditional skills, not replace them. For example, while AI can draft a melody or generate a sketch, dedicate time to practicing your craft manually to keep your technical abilities sharp. Take the time to reflect on the solution or alternatives offered by AI – consciously learn new processes and alternative avenues followed by AI.
4. Overcoming Limited Artistic Intuition
AI bases its outputs on patterns, data, and algorithms. While these are powerful, they may lack the intuitive leaps, imaginative spontaneity, and raw emotional expression unique to human creativity. They are also likely to lack the colloquialisms, cultural quirks and unique blend of stories, myths, rites, rituals and subtle mixes of cues unique to a specific sub-group or target audience.
Solution: Add human layers to AI outputs. Take AI-generated ideas and infuse them with your intuition, storytelling, wisdom, and emotional depth to ensure the final work resonates with your audience.
5. Navigating Ethical Concerns and Ownership
When working with AI, it can become unclear where your contribution ends and where AI’s begins. This raises important questions: Who owns the rights to AI-generated content? How do you ensure your authorship remains intact?
Solution: Be transparent about the use of AI in your work and establish clear terms for ownership. Platforms like Adobe and OpenAI provide guidelines for ethical AI usage that can help clarify these boundaries.
ARTEFICE Model of AI Integration
To help to recall and apply the principles of the model discussed above, we offer the ARTEFICE model as explained in Table 7.2. The acronym ARTEFICE captures the blend of artistry and technology (a nod to “artificial intelligence”), while also invoking creativity, craft, and cleverness—all essential elements of working with AI in creative fields. Each letter represents a stage in the process. Also see Figure 7.9 to help you to recall these principles and to highlight the cyclical or iterative nature of this process throughout the many phases of the creative process.
Table 7.2 ARTEFICE captures some challenges and steps to overcome them
|
Letter |
Stage |
|
A – Articulate Your Voice |
Define your unique artistic style and identity. What makes your work distinct? What emotions, themes, and ideas define you? |
|
R – Review AI Tools Usage |
Evaluate how you use AI. Are you leveraging its strengths effectively, or over-relying on it? Identify opportunities for balance. |
|
T – Tailor Creative Boundaries |
Establish clear boundaries for AI’s role in your process. Decide how much influence AI will have and where human intuition will shine. Clearly define AI’s role. Will it inspire you, assist with execution, or just provide a foundation? |
|
E – Consider/ |
Reflect on authorship and ownership. How will you credit AI contributions? How will you ensure transparency and integrity in your work? How will you check validity of the information/statistics/sources/quotations/other contributions? |
|
F – Fuse AI Outputs with Your Style |
Combine AI-generated content with your unique creative touch. Blend the two seamlessly to create something truly original. Consider the purpose and target audience with care – ensure impact and persuasive power for THAT audience. |
|
I – Invest in Hands-On Practice |
Dedicate time to manual work. Use this to refine your core skills and ensure that AI complements rather than replaces your craftsmanship.
|
|
C – Collaborate for Feedback |
Share your AI-enhanced work with peers, mentors, or your audience. Gather insights to refine and elevate your creations. |
|
E – Evolve Through Experimentation |
Keep pushing boundaries. Experiment with new AI tools, techniques, and workflows. Use each project to grow as a creator. |

By recognizing these challenges and taking steps to address them, you can use AI to enhance your creativity while staying true to your artistic identity. Remember, AI is a partner—not a replacement—for your unique genius.
Harnessing Collective Intelligence: Crowdsourcing and Focus Groups
Leveraging collective intelligence through crowdsourcing and focus groups can be a game-changer – not only by saving R&D funds, being more customer-centric and aligned with customer needs, but also by creating instant fans and life-long supporters in these co-creatives. These strategies tap into diverse perspectives, fostering innovation and ensuring products resonate with target audiences. It also levels the playing field for large corporations with huge R&D budgets and young, lean, not-so-cash-rich start-ups. (see The Idea Evaluation Process: A Complete Guide).
Crowdsourcing Ideas for Innovation: Leveraging the Wisdom of the Crowd
Crowdsourcing involves soliciting ideas, solutions, or feedback from a large group of people, often via the internet. In some cases, companies organize in-person, shorter deadline large-group idea sourcing called Hackathons. This approach democratizes innovation, allowing startups to access a vast pool of creativity and expertise without significant financial investment.
Weighing the Benefits and Challenges of Crowdsourcing
While crowdsourcing offers exciting opportunities, it also comes with potential risks. Consider the pros and cons in Table 7.3 that might make the crowdsourcing worth the effort, or if not considered with care, may deliver risks that may lead to unexpected legal/IP issues and overlooking real winning ideas or the talent to realize them.
Table 7.3: Pros and Cons of Crowdsourcing
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
Unites communities around a shared mission, fostering engagement and brand loyalty. |
Results can be biased depending on the demographics and experiences of the participants. |
|
Provides an efficient method for tackling complex, time-intensive challenges. |
Lack of confidentiality or ownership may lead to intellectual property concerns. |
|
Encourages deeper interaction with users, allowing companies to co-create solutions with their customers. |
Risk of overlooking truly innovative ideas if the loudest voices dominate the conversation or if the right talent isn’t engaged. |
Some success stories in the marketplace from various industries will illustrate that crowdsourcing is a valid and useful method sought by big brands.
Real-World Examples:
Unilever’s Foundry Platform: Unilever launched the Foundry platform to connect with startups and innovators worldwide, seeking solutions for its business challenges. The platform encouraged participants to propose ideas across various areas, including product development, marketing, and sustainability. Watch this video about the Innovators’ Method (https://youtu.be/sGIAdHcitoY) and Unilever’s Foundry Platform here: Innovation through collaboration)
IKEA’s Co-Create Initiative: Early in 2018, IKEA launched Co-Create IKEA, a digital platform focusing on gathering ideas from customers and collaborating with university students on product solutions. Initially the idea was pilot-tested with IKEA employees’ family members, who were invited to co-create new products before opening up to a broader audience.
You can read more about Open Sources and Crowd Idea Sourcing here:
5 Crowdsourcing Examples That Delivered Impressive Business Results
18 Companies that Use Crowdsourcing for New Product Design & Prototype Innovation | Cad Crowd
or for Ikea, here at: IKEA Hackers – Clever ideas and hacks for your IKEA Furniture;
BMW Crowd Innovation here: www.bmwgroup.com/en/innovation/open-innovation/crowd_innovation.html; BMW Crowd Innovation
Heineken’s Open Design See the video here: https://youtu.be/cLxlFsFho7s ( https://youtu.be/cLxlFsFho7s)

Effective Implementation of Crowdsourcing
To implement crowdsourcing effectively:
Define Clear Objectives: Clearly articulate the problem or opportunity to guide participants. What would you like them to achieve? What are the key issues or primary criteria they have to work around?
Choose the Right Platform: Select platforms that align with your industry and target audience. Here are some possible sites: (e.g., Atlan Collective, CadCrowd, Kickstarter, OpenIDEO, HeroX).
Engage the Community: Foster a sense of ownership among participants through regular updates and recognition. Ask participants to share some of their personal stories either via digital platforms (e.g., TikTok, YouTube) or create a special site or part of the competition site where stories can be shared with other participants and their families.
Evaluate and Implement Ideas: Establish criteria for assessing submissions and a process for integrating viable solutions.
Using Focus Groups for Customer Insights:
Gathering Valuable Feedback to Inform Creative Decisions
Focus groups involve guided discussions with selected individuals to gain insights into their perceptions, opinions, and attitudes toward a product or service. This qualitative research method provides depth and context that quantitative data may lack. Focus groups are instrumental in gathering customer insights for product enhancements and new inventions.
For more insights into why and how focus groups help,see : How Focus Groups Drive Product Development – FasterCapital and for more examples: Focus Groups: An In-Depth Exploration on use cases and functions
Real-World Examples:
Pella: Installer-Focused Window Designs
Pella, the Iowa-based window and door maker, designed a mechanism to focus on the pleasure-points for the installer (in this instance adding to the value for the homeowner). Based on observations and responses, Pella’s new window is easy to install from the inside rather than the outside of a property, reducing installation time, increasing safety for workers, and improving efficiency on job sites. By prioritizing installer feedback and installers as customers, Pella successfully streamlined the process while maintaining the quality and durability expected from its brand.
London Buses: Redesigning the Routemaster
In 2007, Transport for London initiated the redesign of the iconic Routemaster bus, starting with a widely announced competition for designers. They conducted focus groups with passengers, drivers, and other stakeholders to gather feedback on various design aspects, including accessibility, comfort, and aesthetics. Insights from these discussions led to features like low-floor boarding, increased seating capacity, and improved energy efficiency in the new buses. (Bing Videos). See the crowd-sourcing of ideas for the iconic London Buses here, at www.dezeen.com/2008/12/19/a-new-bus-for-london-by-aston-martin-and-foster-partners/. The judges indicated these next stages, based on the excellent entries received: “The aim of our competition was to harvest a range of creative ideas for a bus fit for the 21st century. We will now pass the best designs and concepts on to bus manufacturers, so they can be developed into final design proposals.

See more about the London Bus Redesign here”: A new bus for London competition winners announced | Dezeen; See some comments about the focus groups and pilot testing here: The new London Routemaster launched | Engineering and Technology Magazine
Starbucks: Enhancing the In-Store Experience
Starbucks has used focus groups to refine its in-store experience. By engaging with customers in these settings, the company gathered feedback on store ambiance, product offerings, and service quality. These inputs informed decisions such as store layout modifications, introduction of new menu items, and adjustments to customer service protocols, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
LEGO: Developing the Mindstorms Series
LEGO employed focus groups comprising children, parents, and educators during the development of its Mindstorms series. These sessions provided valuable insights into user interactions, educational value, and design preferences. The feedback guided improvements in the product’s usability, instructional materials, and feature set, contributing to the success of the Mindstorms line. (See Fig 7.12 for a sample of and link to the Mindstorms Robotic series that helps kids to intuitively learn coding).
See the “Robots are coming” Video to inspire players at: https://d14l911dvnjir8.cloudfront.net/public/e6/75/e67567c4-132f-4566-929d-bf3a995e1618_11be7813-fd75-4b78-979a-a3d400c43d6d_nl-nl_2_2560.mp4#t=0.1
McDonald’s: Revamping the Menu
McDonald’s has conducted focus groups to explore customer reactions to potential menu changes. For instance, when considering healthier options, the company gathered feedback on taste preferences, pricing, and perceived health benefits. This approach helped McDonald’s introduce new items that aligned with customer desires while maintaining brand identity.
Procter & Gamble:
As a leader in consumer goods, Procter & Gamble (P&G) has long relied on focus groups to refine and innovate its products.
Pampers Diapers: P&G conducted extensive focus groups with parents to understand key concerns such as absorbency, comfort, and ease of use. The insights led to the development of diapers that met these critical needs, helping Pampers become a market leader.
Beauty and Personal Care Products: P&G’s flagship brands, including Olay and Pantene, actively engage consumers in testing new formulations and packaging designs. Feedback from focus groups influences not only product performance but also branding and marketing strategies, ensuring alignment with customer expectations. See more details here: Focus Groups: An In-Depth Exploration on use cases and functions)
These examples demonstrate how focus groups can provide deep insights into customer preferences and behaviours, guiding companies in making informed decisions about product development and enhancements.
Best Practices for Conducting Insightful Focus Groups
- Define Clear Objectives: Determine what you aim to learn from the focus group.
- Select Participants Carefully: Choose individuals who represent your target market.
- Develop a Discussion Guide: Prepare open-ended questions to steer the conversation.
- Create a Comfortable Environment: Ensure participants feel at ease, to encourage honest feedback.
- Facilitate, Don’t Lead: Guide the discussion without influencing responses.
- Analyze and Act on Insights: Review the feedback to identify patterns and inform decision-making.
By effectively harnessing collective intelligence through crowdsourcing, focus groups, and various collective collaborative forums (e.g. hackathons), young entrepreneurs can drive innovation and ensure their offerings align with market needs. Embracing these strategies fosters a culture of inclusivity and continuous improvement, essential for startup success.
You can find a number of real-world cases at this URL to learn from the best in market: 101 Case Studies Exploring Innovation | by Mark Bridges | Medium
PRIME Framework to Evaluate Concepts & Ideas
The PRIME Analysis Tool is a heuristic (mental shortcut) designed for the initial evaluation of business concepts before developing a comprehensive business plan. It assists in assessing venture opportunities by focusing on key aspects such as product feasibility, market potential, and financial viability
The PRIME Framework to Evaluate Ideas Generated by Collective Intelligence Forums
The PRIME framework evaluates ideas across five critical dimensions, providing a comprehensive view of their viability and strategic alignment. PRIME stands for:
Potential – What is the scale of the opportunity? Does the idea address a significant problem or an untapped market?
Return – What are the expected financial or strategic gains?
Investment – What resources, in terms of time, money, and expertise, are required to implement the idea?
Motivation – How well does the idea align with the organization’s mission, vision, and priorities?
Expertise – Does the team have the skills and capacity to execute the idea successfully?

Designing Effective Focus Groups: Alpha (α) & Beta (β) Testing Stages
To maximize the effectiveness of focus groups in product development, they should be structured into two key stages: Alpha Testing and Beta Testing. Each stage answers different critical questions to ensure products are developed and refined based on real user insights.
α Alpha Test: Early-Stage Exploration
This stage focuses on ideation and problem validation before major investments are made.
Define Objectives Clearly – Establish what you need to learn (e.g., consumer pain points, feature desirability).
Key Questions to Answer:
- What unmet needs exist in the market?
- What are customers’ biggest frustrations with current solutions?
- What features or improvements would they find most valuable?
Select a Targeted Group – Include early adopters, industry experts, or users who experience the problem first-hand.
Facilitate Open-Ended Discussion – Use broad questions to explore unmet needs, perceptions, and expectations.
Key Questions to Answer:
- What first impressions do you have about this idea?
- What aspects of this concept excite or concern you?
- How would you describe the ideal solution to this problem?
Analyze Initial Feedback – Identify patterns, recurring pain points, and early insights for refinement.
Key Questions to Answer:
- What common themes emerged from participants?
- Are there clear demand signals for specific features?
- How does this feedback influence the next iteration?
β Beta Test: Refining & Validating Solutions
This stage focuses on testing product iterations, usability, and market fit before launch.
Refine Participant Selection – Include a mix of power users and general consumers to get diverse perspectives.
Test Specific Features & Prototypes – Present tangible concepts for detailed feedback.
Key Questions to Answer:
- How intuitive is the product or feature to use?
- What challenges did users experience while interacting with it?
- How does this compare to their current solutions?
Gather Usability Insights – Observe interactions, pain points, and workflow challenges.
Key Questions to Answer:
- What improvements would make this product easier to use?
- Did users encounter any friction points?
- Were there any unexpected benefits or drawbacks?
Refine Based on Data – Use feedback to finalize design, messaging, and positioning.
Key Questions to Answer:
- What features should be adjusted, removed, or enhanced?
- Does the product deliver on its promised value?
- Is this product ready for launch, or do further iterations need testing?
By structuring focus groups into Alpha and Beta phases, innovators, creatives, and genii ensure they gather meaningful insights at the right time, improving product-market fit before a full-scale launch.
Partnering for Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Clarifying Your Goals Before Seeking a Partner
Before seeking a partnership or joining with another venture, be crystal clear on what you want to achieve. Ask yourself:
What’s my main objective—expanding into new markets, gaining access to new technology, gaining reputation through established providers, or cutting costs?
What unique value can I bring to a potential partner in return?
Having well-defined goals helps you identify partners that truly align with your vision.
Equally important is a self-assessment. Take a hard look at your company’s strengths, weaknesses, and any gaps in your product or service offering. Understanding where a partnership can add the most value ensures you enter collaborations strategically, with clear expectations and purpose. Shared values such as similar business ethics; and complimentary communication styles will aid progress. Incompatible cultures and work ethics will lead to friction and hinder progress.
Best Practices for Strong, Lasting Partnerships
Successful partnerships don’t happen by chance—they’re built on a foundation of trust, clear communication, and shared purpose. To create a collaboration that thrives, consider these best practices:
Define Roles and Responsibilities from Day One
- Make sure every partner knows their role, what they bring to the table, and how decisions will be made. Clearly outlining contributions, authority, and accountability prevents confusion and keeps everyone aligned. A shared vision and mission statement serves as a guiding force when tackling challenges or making strategic moves.
Keep Communication Open and Transparent
- Consistent, honest conversations are the lifeblood of any strong partnership. Schedule regular check-ins to discuss progress, roadblocks, and opportunities. Encourage open dialogue and active listening. Leverage collaboration tools to streamline communication and knowledge sharing, ensuring everyone stays on the same page.
Trust and Respect: The Non-Negotiables
- Reliability and integrity are essential. Follow through on commitments, respect each other’s expertise, and foster a culture of mutual support. Recognize and celebrate wins together, but also learn from setbacks as a team. Strong partnerships are built on resilience.
Plan for Conflict Before It Happens
- Disagreements are inevitable, but how you handle them determines whether a partnership thrives or falls apart. Establish a clear conflict-resolution framework that prioritizes open discussion, fair compromise, and win-win solutions. If necessary, bring in a neutral mediator to keep things constructive.
Commit to Continuous Growth
- Regularly assess the partnership’s impact and effectiveness. Are you meeting your goals? Where can you improve? Adaptability is key—successful partnerships evolve as business landscapes shift. Conduct periodic reviews and make strategic adjustments to keep the collaboration strong and aligned with long-term objectives.
By putting these principles into action, businesses can build powerful, enduring partnerships that fuel innovation, drive growth, and create value for all involved.
The Partnership Success Pyramid (PSP)
The PSP is a framework that helps organizations assess and build strong, sustainable partnerships by focusing on key success factors. It is typically structured in three levels, each representing a crucial component of a thriving collaboration.
The Three Levels of the Partnership Success Pyramid
1. Foundation – Alignment & Compatibility (The Base)
This level ensures strategic alignment between partners. Without a strong foundation, partnerships may lack stability and fail to create lasting value.
- Mission & Core Values: Are both organizations culturally aligned and working toward a shared purpose?
- Partnership Goals & Intended Outcomes: Does the collaboration serve mutual interests and long-term vision?
- Legal & Compliance Fit: Are regulatory and contractual requirements clear and manageable?
2. Structure – Capabilities & Resources (The Middle)
Once alignment is established, the focus shifts to resources and execution capabilities that determine the feasibility of collaboration.
- Quality of Solutions & Innovation Capability: Does the partner bring unique value through products, technology, or expertise?
- Scale & Capacity of Production: Can they meet market demand efficiently?
- Operational Compatibility: Are processes and systems compatible for seamless integration?
- Capabilities & Competencies: Can they provide the right levels of staff (senior and less senior) at the right time in the project life? Do they have the creative, technical and decision-making leadership and support necessary for thriving, highly productive teams?
3. Growth – Performance & Longevity (The Peak)
This level measures the long-term viability and impact of the partnership. Strong partnerships evolve, scale, and deliver measurable success.
- Track Record & Results: Does the partner have a history of delivering on commitments? Do they stick to the deadlines, regulatory requirements and
have the technical (software and tacit capabilities) to deliver on this project? - Financial Stability & Profitability: Can they sustain a long-term relationship without financial risks?
- Brand Strength & Network Influence: Will their reputation and connections open new market opportunities?

How to Apply the Partnership Success Pyramid
- Use It as an Assessment Tool – Before entering a collaboration, evaluate a potential partner against the three levels.
- Ensure All Levels Are Strong – A weak foundation (misaligned goals) or structure (lack of resources) can cause failure.
- Continuously Review & Adjust – Partnerships should be re-evaluated periodically to ensure continued alignment and effectiveness.
(See the DIY Worksheet for partner assessment in the Toolshed)
60-second Executive Summary (60 ES) of Chapter 7 – PARTNERSHIPS-focus
Innovation thrives at the intersection of human intelligence and technological augmentation. This chapter explores how AI, collaborative models, and structured frameworks drive business success in a fast-evolving landscape. Diverse perspectives fuel stronger decision-making. Businesses that integrate varied expertise and viewpoints enhance problem-solving, creativity, and adaptability. AI can be gainfully employed to enhance human capabilities by automating tasks, analysing data at scale, and offering predictive insights. It acts as a powerful tool for efficiency rather than a replacement for human expertise. AI doesn’t just automate; it accelerates ideation by identifying patterns, generating insights, and sparking creative breakthroughs in innovation processes. AI must be strategically embedded into business processes through Automation, Real-time insights, Technology scaling, Efficiency, Feedback loops, Intelligent adaptation, Context awareness, and Ethical governance (AFTEFICE model).
Further, businesses leverage large-scale public input to validate ideas, uncover trends, and refine products through real-time engagement. Direct customer feedback remains crucial. AI-assisted focus groups allow for deeper sentiment analysis, enhancing product-market fit. To get the best in terms of brainpower and resources, collaboration with AI-driven tools, strategic partners, and global networks fosters long-term resilience, enabling businesses to adapt, innovate, and scale effectively and to deliver sustainable competitive advantages.
References
Atlan. (December 13, 2023). Collective intelligence: Concepts and reasons to choose it. https://atlan.com/collective-intelligence/
Bridges, M. (September 25, 2024). 101 Cases Exploring Innovation. Medium. https://mark-bridges.medium.com/101-case-studies-exploring-innovation-bec555f41509
Davis, B. (January 22, 2023) An Extremely Intelligent Lava Lamp: Refik Anadol’s A.I. Art Extravaganza at MoMA Is Fun, Just Don’t Think About It Too Hard. Artnet. https://news.artnet.com/art-world/refik-anadol-unsupervised-moma-2242329
Gero, J. S., & Maher, M. L. (2020). AI and Creativity in Design Processes. Artificial Intelligence in Engineering, 11(3), 171–180
Gibson, C. B., & Gibbs, J. L. (2006). Unpacking the concept of virtuality: The effects of geographic dispersion, electronic dependence, dynamic structure, and national diversity on team innovation. Administrative Science Quarterly, 51(3), 451-495.
Heavens, J. (2023). Ethics in AI: Ownership and Authorship in the Age of Machine Learning. International Journal of Ethics in Technology, 45(2), 145–162.
Human, S.E., Clark, T., Baucus, M.S. & Eustis, A.C. (2004). Idea or Prime Opportunity? A Framework for Evaluating Business Ideas for New and Small Ventures. Journal of Small Business Strategy 15(1). https://libjournals.mtsu.edu/index.php/jsbs/article/view/9
Hundschell, A., Razinskas, S., Backmann, J., & Hoegl, M. (2022). The effects of diversity on creativity: A literature review and synthesis. Applied Psychology, 71(4), 1598–1634. https://doi.org/10.1111/apps.12365
Kramer. M, (January 22, 2025). Integrating AI-Enabled Insights to Guide Innovation. All Things Innovation. https://allthingsinnovation.com/content/integrating-ai-enabled-insights-to-guide-innovation
Leroy, H., Buengeler, C., Veestraeten, M, Shemla, M., & Hoever, I.J. (2022). Fostering Team Creativity Through Team-Focused Inclusion: The Role of Leader Harvesting the Benefits of Diversity and Cultivating Value-In-Diversity Beliefs. Group & Organization Management. 47:4, 798-839. DOI: 10.1177/10596011211009683
Lorenzo, R., Voigt, N., Tsusaka, M. & Krentz, M. (2018) How Diverse Leadership Teams Boost Innovation. Boston Consulting Group. https://www.bcg.com/publications/2018/how-diverse-leadership-teams-boost-innovation
Makarov, A. (November 19, 2024). 12 Augmented Reality Technology Trends of 2025: New Milestones in Immersive Innovations. Mobidev. https://mobidev.biz/blog/augmented-reality-trends-future-ar-technologies
Maznevski, M. L., & Chui, C. (2018). Leading global teams. In M. E. Mendenhall, J. Osland, A. Bird, G. R. Oddou, M. J. Stevens, M. L. Maznevski, & G. K. Stahl (Eds), Global leadership (3rd ed., pp. 153–174). Routledge.
Patel, K. (2020). Finding Harmony: Balancing Human and AI Creativity. Creative Process Journal, 15(1), 112–127.
Pirola-Merlo, A., Härtel, C., Mann, L., & Hirst, G. (2002). How leaders influence the impact of
affective events on team climate and performance in R&D teams. The leadership quarterly, 13(5),
561-581.
Scott, C. P., & Wildman, J. L. (2015). Culture, communication, and conflict: A review of the global virtual team literature. In J.L Wildman & R.L. Griffith (Eds). Leading global teams: 13-32. Springer.
Stahl, G.K., Maznevski, M.L. (2021) Unraveling the effects of cultural diversity in teams: A retrospective of research on multicultural work groups and an agenda for future research. Journal of International Business Studies 52, 4–22. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41267-020-00389-9.
Thomas, D. C., Ravlin, E. C., & Wallace, A. W. (1996). Effect of cultural diversity in work groups. Research in the Sociology of Organizations, 14(1): 1–33.
Wilson, H. J., & Daugherty, P. R. (July-August, 2018). Collaborative intelligence: Humans and AI are joining forces. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2018/07/collaborative-intelligence-humans-and-ai-are-joining-forces
Some sources for your extra reading and those interested in AR.
https://partnernomics.com/evaluating-potential-partners/
Just for those who love learning or music or AR https://youtu.be/6hScacmPAek
OR here a demo of AR for those (like me) who is lost on campus waaaay too often. https://youtu.be/VmROm6nbElA.
AR for Brands 12 Augmented Reality Technology Trends for Business to Watch in 2025

