4.4 Digital solutions
Digital health can enhance efficiency, reduce costs and support healthcare workers and consumers. Digital health solutions will not decrease the need for clinicians and their expertise (Kolasa & Kozinski, 2020). Digital health solutions offer the potential to create value by supporting clinical decision-making more effectively. Further, they can support the delivery of safer treatments and efficiency gains through innovative models of care delivery, reduction of delays and more consumer- and clinician-friendly organisation of the healthcare system.
The administrative processes used by healthcare providers can be time-consuming to complete and often involve the collection of similar or the same information multiple times. Streamlining administrative processes can reduce delays for administrative staff, clinicians and consumers. Optimising resource allocation is another way that value can be attained using health information systems and digital tools. With AI there are opportunities to enhance workforce allocation and improve diagnosis reliability (Scott et al., 2021). By analysing various data points, such as patient volumes, case mix, patient acuity, staff schedules, skill sets and patient needs, AI tools can optimise workforce allocation. Predictive analytics can forecast demand for healthcare services across different departments and timeframes, allowing health service managers to adjust staffing levels. Workforce management systems can also consider factors like staff preferences, qualifications and availability to create schedules that reduce overtime, burnout and maintain staff wellbeing.
Scenario analysis and what-if modelling using advanced data analytics or simulation packages can also help healthcare teams test different scenarios, like adding another operating theatre, before making real changes. For example, staff can input data into the software to see how adding a new theatre affects things like surgery wait times and staff workload. By trying out different scenarios, teams can figure out the best time to make changes and improve how the department works. These packages help the analysis and optimisation of healthcare processes, reducing bottlenecks and improving resource allocation and flow. Tools can be used for tasks like designing layouts for new facilities, testing different staffing levels, predicting wait times and assessing the impact of changes in workflow or equipment.
Preventative care through data-driven insights such as measures of cholesterol, blood pressure, education, lifestyle history and genetics can help identify individuals at risk of cardiovascular disease. Based on this data clinicians could support individuals to adopt preventive measures such as medication, lifestyle and dietary changes, and smoking cessation to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
For digital health to add value the World Bank (2023) has identified three required areas to ensure that the value and benefits are available to all, including underserved populations. They state that to embrace an approach where digital is a routine part of health – ‘digital-in-health’ – the three essential areas for investment by governments in digital and data are to prioritise, connect and scale (World Bank, 2023). Figure 4.4 shows the elements that are included in each of these areas.
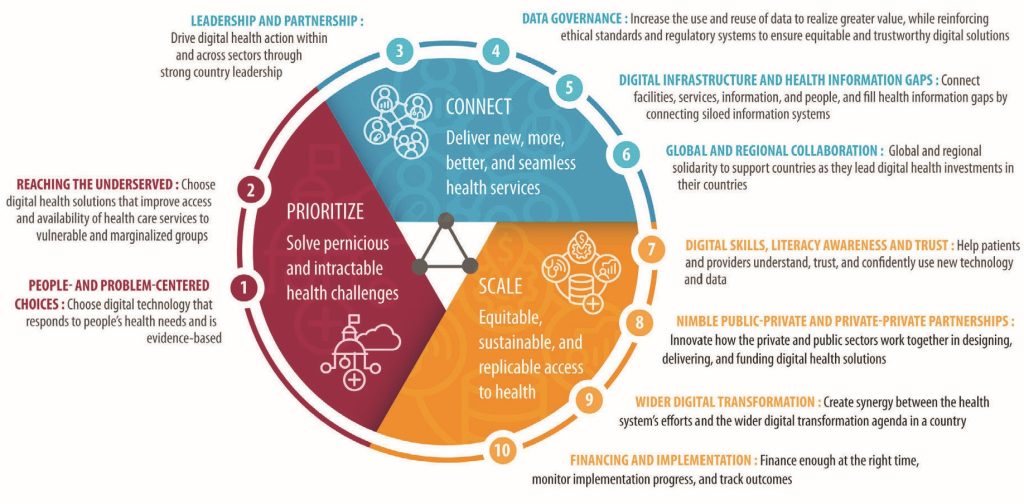
Source: Digital-in-health: Unlocking the value for everyone. Summary. World Bank (2023). Washington DC. Used under CC BY 4.0.

