Module 2.3 Effective and efficient searching

Once you have developed a search strategy and selected your clinical resource or database, the next step is to run your search. You can apply additional advanced search techniques and limits depending upon the features available in the clinical resource or database.
Each clinical resource may require a different search strategy. Use the search terms (from your PICO) to identify the best subject headings or keywords.
Each clinical resource provides a range of search tools beyond Boolean operators. While you may not necessarily use all these tools (or limits) in every search that you undertake, it is useful to know that they exist as a means of improving or refining your results.
See this video Online Research Tips for Effective Searching, then work through the slides and activities below.
Databases like Medline, Embase and CINAHL have their own thesaurus. You can use the thesaurus to identify terms (sometimes referred to as Subject Headings ) which will help to refine your search. Medline uses specialised MeSH Medical Subject Headings. Watch this video demonstrating how to search Medline using both keywords and Subject Headings.
Other ways to filter search results are by publication year, language and publication type eg journals, conference papers.
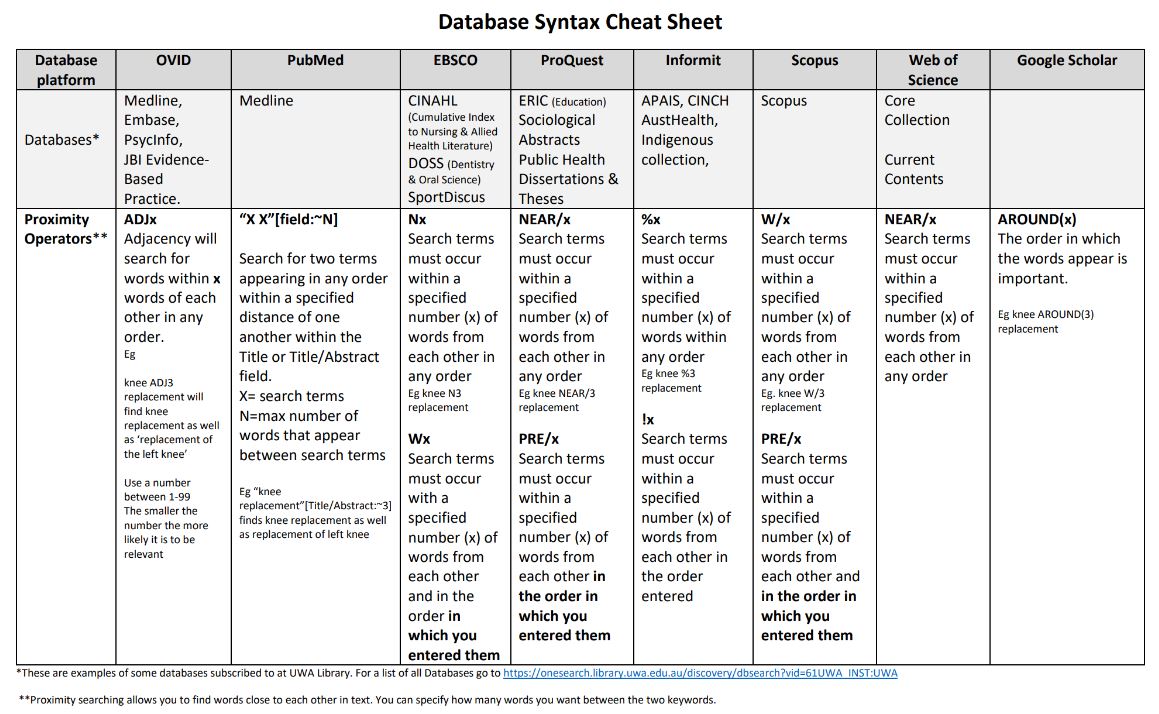
See this Database Syntax Cheat Sheet for the syntax used across the various database platforms Ovid, Ebsco, ProQuest and databases Medline, Embase, CINAHL etc.
What type of question do you have? Having the question type in mind when you start, will help you determine what kind of evidence will best answer your question. Some clinical resources, such as PubMed/Medline, provide particularly sophisticated and specialised limits and filters.
The National Library of Medicine maintains and publishes the Medline database, which indexes the medicine, dentistry, nursing, allied health and veterinary science literature. The most popular platforms for searching Medline are PubMed (free) and Ovid.
PubMed is comprised of citations from the Medline database, as well as other life science journals and online books not included in Medline.
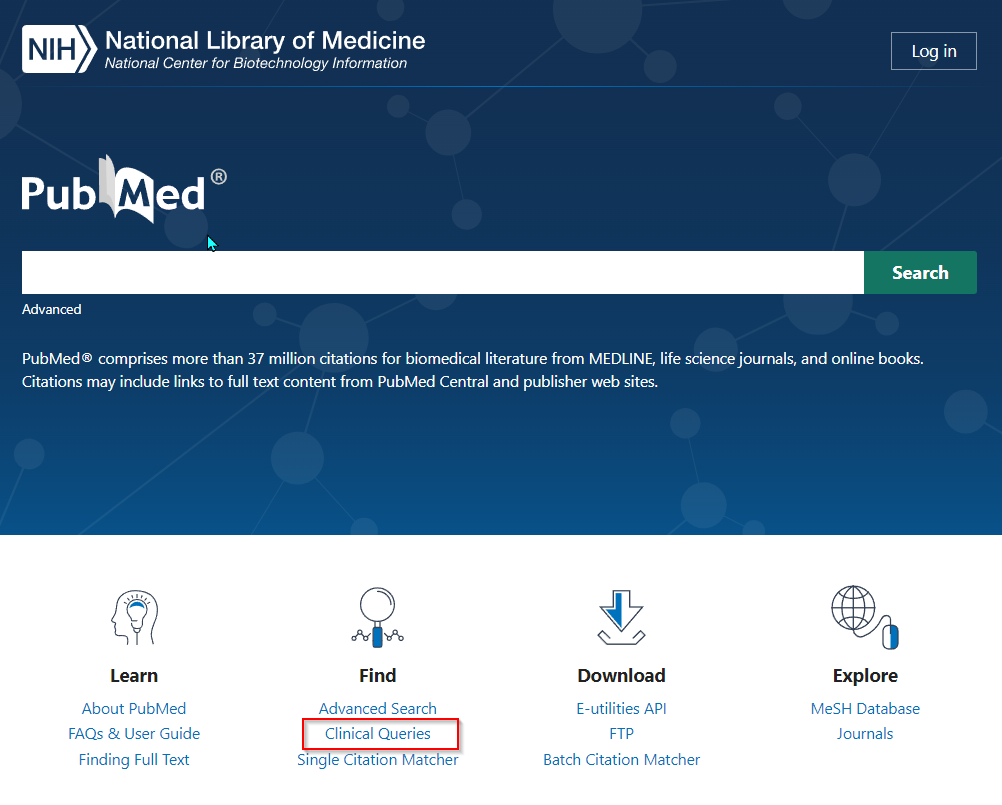
PubMed Clinical Queries is a tool created for clinicians, to quickly find evidence in PubMed by restricting search results using predefined and validated search filters for clinical study categories : Therapy, Diagnosis, Etiology and Prognosis.
Access PubMed Clinical Queries directly or via the Clinical Queries link on the PubMed homepage:
You can search for Clinical Studies, by entering the main concept search terms from your PICO and then selecting the appropriate filter from the drop down box:
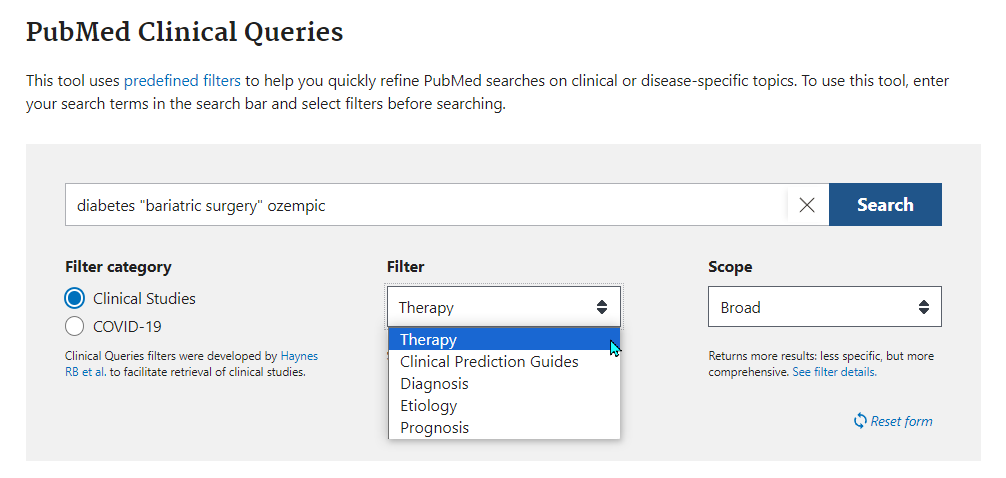
The search filter for Therapy is:
((clinical[Title/Abstract] AND trial[Title/Abstract]) OR clinical trials as topic[MeSH Terms] OR clinical trial[Publication Type] OR random*[Title/Abstract] OR random allocation[MeSH Terms] OR therapeutic use[MeSH Subheading])
See all search filters used by PubMed Clinical Queries.
See this tutorial on using PubMed Clinical Queries for more information and this PubMed Online Training.

